There’s little worse than missing an important call or text because your iPhone was in Do Not Disturb mode or because the Mute switch was engaged. If there are certain people—a spouse, parent, or child—whose calls and texts you always want to break through the cone of silence, iOS has a solution: Emergency Bypass. When enabled for a particular contact’s ringtone or text tone, Emergency Bypass ensures the sound and vibration will happen regardless of Do Not Disturb or the Mute switch position. To set up Emergency Bypass, edit the person’s contact card in the Phone or Contacts app, tap Ringtone, and enable Emergency Bypass. You can turn on Emergency Bypass separately for calls in the Ringtone settings and for texts in the Text Tone settings. And remember, you can always set someone’s tone to None and enable a vibration instead to ensure Emergency Bypass doesn’t allow a call to interrupt a movie, play, or concert.


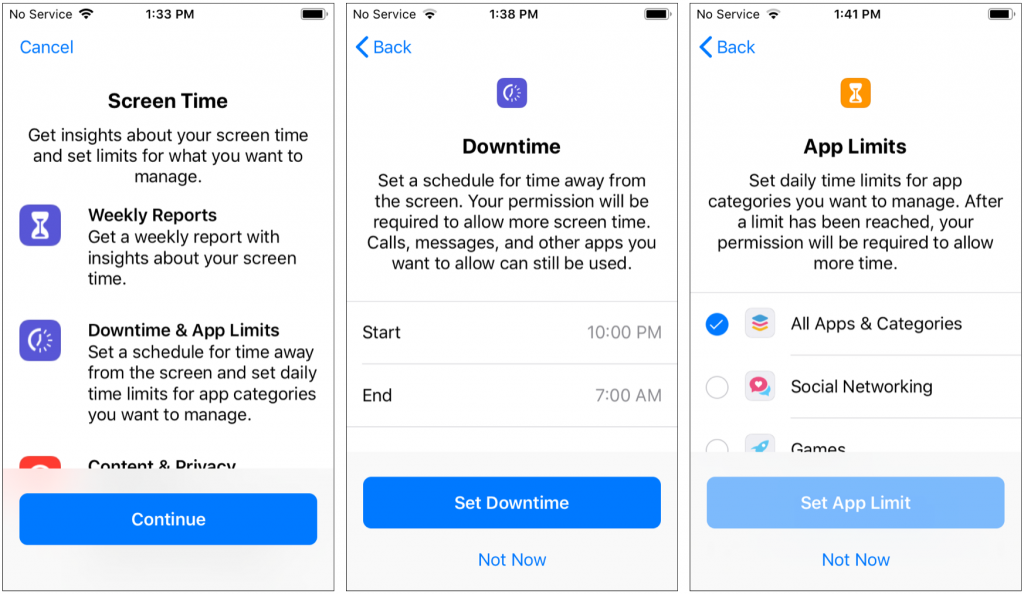
 Downtime is useful for blocking all device usage during a time when your child should be sleeping, doing homework, or just not using the screen. You can set only one time period, so if you want to control usage on a more complex schedule, you’ll need to do that in another way.
Downtime is useful for blocking all device usage during a time when your child should be sleeping, doing homework, or just not using the screen. You can set only one time period, so if you want to control usage on a more complex schedule, you’ll need to do that in another way.


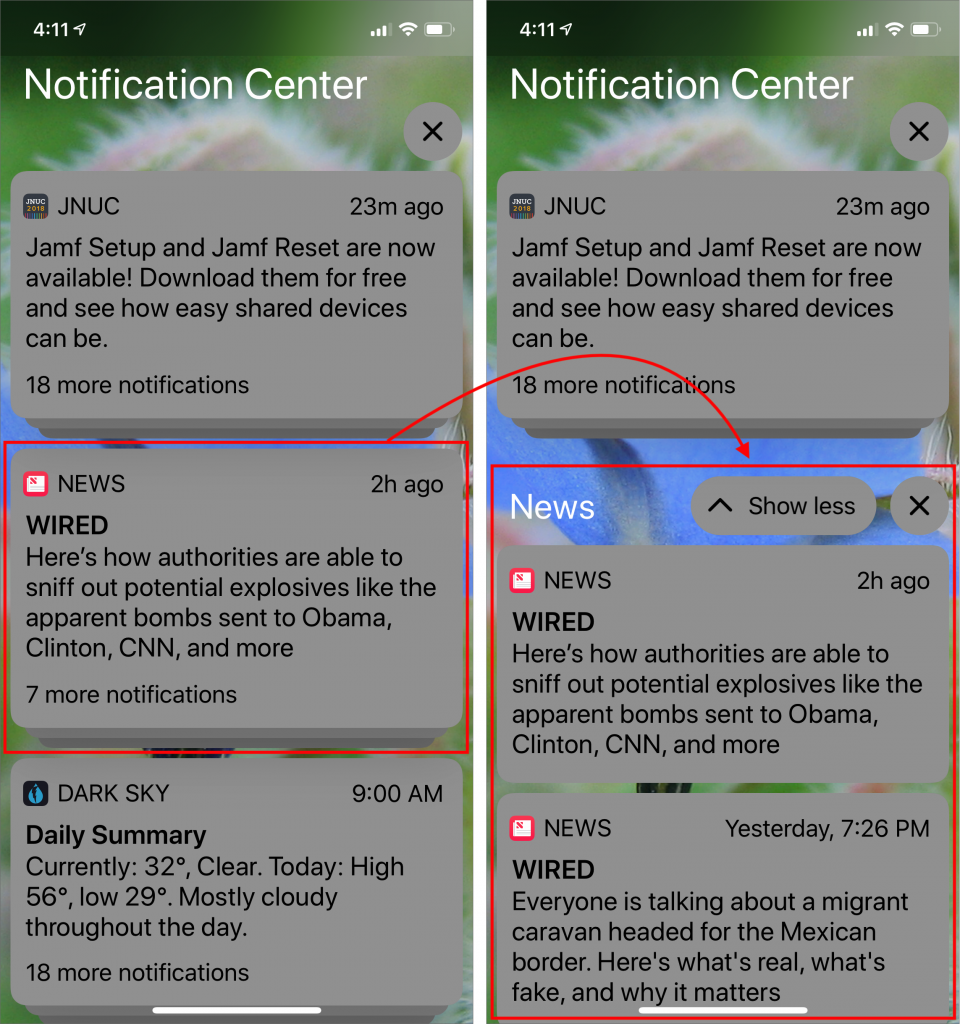






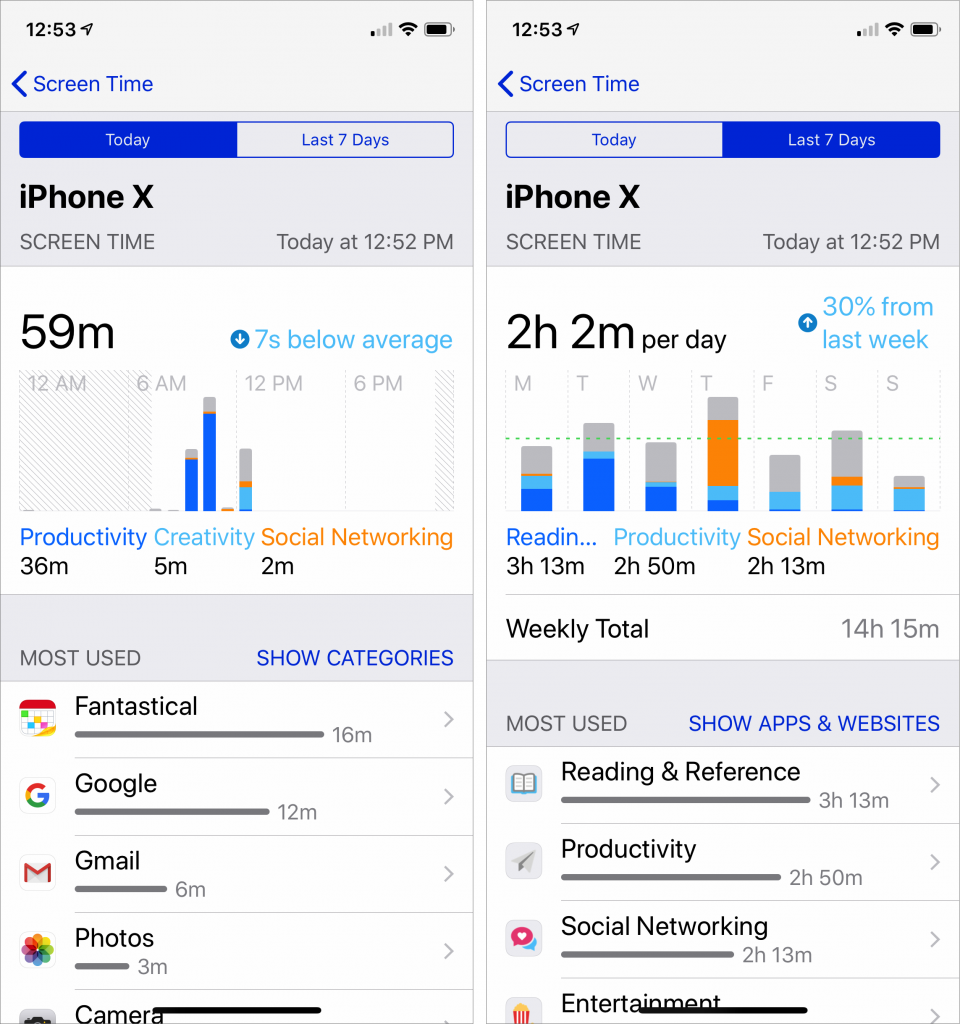


 In the “it’s about time” department, iOS 12 beefs up Do Not Disturb so it works more the way people do. When you bring up Control Center and force-touch the Do Not Disturb button, it expands to let you turn on Do Not Disturb for 1 hour, for the rest of the day, or until you leave your current location. The beauty of these new options is that they disable Do Not Disturb automatically so you don’t have to remember—and potentially miss important notifications. Plus, a new Bedtime option in Settings > Do Not Disturb dims the display and silences overnight notifications until you unlock your device in the morning.
In the “it’s about time” department, iOS 12 beefs up Do Not Disturb so it works more the way people do. When you bring up Control Center and force-touch the Do Not Disturb button, it expands to let you turn on Do Not Disturb for 1 hour, for the rest of the day, or until you leave your current location. The beauty of these new options is that they disable Do Not Disturb automatically so you don’t have to remember—and potentially miss important notifications. Plus, a new Bedtime option in Settings > Do Not Disturb dims the display and silences overnight notifications until you unlock your device in the morning.
