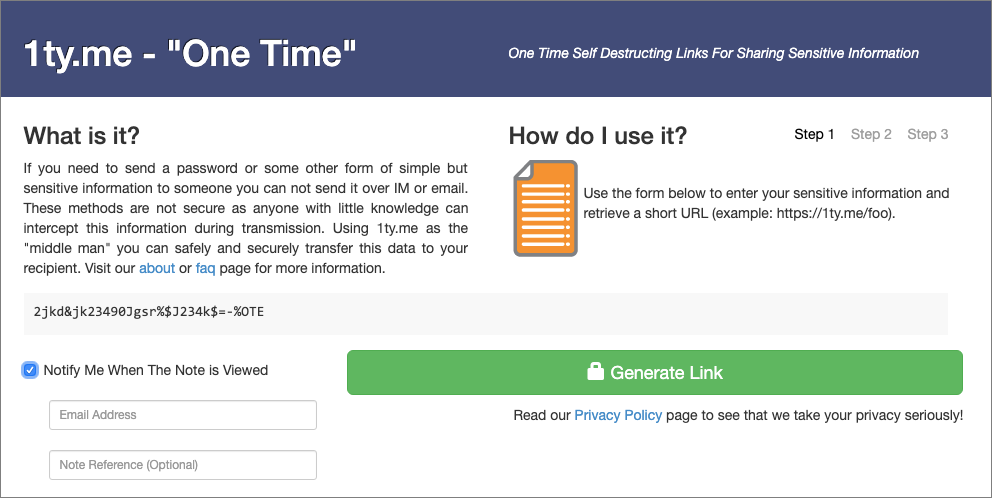
One of the big no-nos with passwords is sending them to other people as plain text in email or a text message conversation. You presumably trust your recipient with the password, but what if their email was hacked or phone stolen? Instead, always use a site like 1ty.me or One-Time Secret, which lets you turn a password into a Web link that can be opened only once. (Not sure about those sites, we have built our very own password sharing site, secret.creativetechs.com that you can use.) Send that link to the recipient, and when they get the password out, they can store it in a secure password manager like 1Password or LastPass.
(Featured image by Kristina Flour on Unsplash)